Did you know seborrheic dermatitis (SD) and dandruff impact half of the adult world? These common conditions on the scalp look similar but are different. Knowing how seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff differ is important for treating them right. This article will talk about what sets these two skin issues apart. We’ll look at their symptoms, causes, and how we can treat them.
Key Takeaways
- Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff affect up to 50% of adults.
- Understanding the differences is key to managing symptoms effectively.
- Both conditions often coexist but require different approaches for treatment.
- Men are more affected by both conditions than women.
- Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
Understanding Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin issue. It mostly affects the scalp, face, and upper chest. These areas have lots of oil-producing glands. People with this condition see greasy, yellowish scales, red rashes, and sometimes flaking. An itchy scalp is common and can be quite bothersome.
What Is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
This skin problem shows up as oily, scaly patches and red rashes. It’s often linked to too much Malassezia yeast on the skin. Both adults and infants can get it, with babies developing cradle cap. This baby version usually clears up by 8 to 12 months. Things like stress, hormones, and the weather can make it worse.
Common Symptoms and Presentation
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- Red or inflamed skin
- Flaky scales on the scalp and other areas
- An itching feeling
Sometimes, seborrheic dermatitis goes away on its own after a few weeks or months. Handling it often involves self-care and medicated treatments. Certain shampoos recommended by doctors can help. They have ingredients like selenium sulfide or ketoconazole, which fight yeast and inflammation.
What Is Dandruff?
Dandruff is a common scalp issue that causes white-to-yellowish flakes to shed. These flakes fall from the scalp onto clothing or hair. It’s different from seborrheic dermatitis because it doesn’t cause inflammation. Having dandruff can make someone feel self-conscious, even though it’s not a serious health problem.
Defining Dandruff and Its Characteristics
Half of all people will deal with dandruff at some point. The flakes are usually dry and might make your scalp itch a little. They are found at the base of hairs but don’t cause red or sore skin. Dandruff is more common in adults but can happen at any age. It’s more annoying than dangerous to your health.
Typical Symptoms of Dandruff
Some typical symptoms of dandruff include:
- White or oily flakes on the scalp
- Mild itchiness that is not extreme
- The presence of flakes on clothing
The issue isn’t just physical. It can make people feel less confident. But if caught early, dandruff can be managed. This helps improve how people see themselves.
Comparing Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Dandruff
When looking at seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, there are clear differences in how severe they are and the symptoms they cause. Seborrheic dermatitis is a long-term type of eczema. It mostly affects areas with a lot of oil glands like the scalp, nose, and upper back. Dandruff, however, is less severe and usually only found on the scalp without visible swelling.
Let’s talk about the symptoms. Seborrheic dermatitis often shows up as scaly patches that are yellow or red. They come with a lot of itching, swelling, and redness. On the other hand, dandruff flakes tend to be white or yellowish. Smaller flakes might suggest a dry scalp, not just dandruff. The irritation and flaking from a dry scalp can look a lot like dandruff, making it tricky to tell them apart.
Now, let’s dig into what causes these conditions. Malassezia, a type of fungus, and too much oil can lead to seborrheic dermatitis. Things like hormone changes, a weak immune system, and stress can raise your risk for it. Dandruff, seen in up to 50% of people, might come from similar issues like too much skin oil or stress.
| Feature | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Dandruff |
|---|---|---|
| Severity | Chronic condition with inflammation | Milder, primarily scalp-focused |
| Flake Color | Yellow or red patches | White or yellowish flakes |
| Associated Symptoms | Itching, swelling, inflammation | Irritation, minimal inflammation |
| Common Causes | Oil production, malassezia irritation | Excess oil, recovery from stress |
| Population Impact | Affects 3% to 5% of U.S. population | Affects up to 50% of population |
Comparing seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff shows why it’s key to know their differences. Knowing them helps us treat these conditions better. This means treatments can be more specifically designed for what you need.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Understanding seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff involves knowing their causes. Many elements impact these conditions, including what’s inside us and what’s around us.
Intrinsic Factors
Hormones, especially androgens, are a major internal factor. They affect how much oil our skin makes, which can cause seborrheic dermatitis. People’s susceptibility can also come from their genes, skin type, or how their skin defends itself. Furthermore, having certain skin issues can make problems worse, highlighting the need to look at one’s overall health.
Environmental Factors
The environment around us can also play a part. Humid weather might help fungi grow, especially Malassezia yeast which lives on our skin. Changes in the weather can make our skin more or less moist, causing discomfort. Also, things that irritate the skin, like strong soaps or allergens, can make everything harder to manage.

| Factor Type | Example Factors |
|---|---|
| Intrinsic | Hormonal changes, genetic predisposition, skin type |
| Environmental | Climate, exposure to irritants, fungal infections |
Common Scalp Conditions Associated with Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff
Millions suffer from scalp issues like seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff. These conditions can be uncomfortable and cause embarrassment. Knowing about them helps us manage them better.
Dandruff often starts after puberty and is more common in men. It might show deeper health concerns, including stress or hormonal shifts. Knowing this can lead to better treatment. Seborrheic dermatitis, on the other hand, is more severe. It causes redness, irritation, and flaking, not just on the scalp but also other oily body parts.
Babies sometimes get a form of seborrheic dermatitis known as cradle cap, which usually goes away after a few months. In older kids, a fungal infection called scalp ringworm can cause itchy patches and bald spots. This mainly affects the young and needs quick treatment to stop it from spreading.
Around half of people with psoriasis have it on their scalps. It shows up as thick red patches with silvery scales. This can be uncomfortable and may lead to hair loss.
Here’s a table that breaks down these scalp conditions:
| Scalp Condition | Age of Onset | Symptoms | Common Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dandruff | Post-puberty | Flaking, itching | Shampoos, stress management |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Late adolescence | Redness, irritation, flakes | Medicated shampoos, natural remedies |
| Cradle Cap | Infancy | Flaky, scaly patches | Gentle cleansing |
| Scalp Ringworm | Childhood | Itchy patches, bald spots | Antifungal treatment |
| Psoriasis | Variable | Thick, red patches with scales | Topical treatments, phototherapy |
Each condition comes with its own set of challenges. Correct diagnosis is key. It ensures that the right steps are taken for management and support. For more details on dandruff causes and how to manage it, check out this guide.
Diagnosis of Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff
To find out if someone has seborrheic dermatitis or dandruff, doctors look closely at the symptoms. They check the skin’s appearance and ask many questions. This helps them understand the issue better. The location and look of the skin problem are key clues. Seborrheic dermatitis often appears in areas with more oil, like the scalp, face, and chest.
Clinical Presentation and Evaluation
Doctors start by checking the scalp and other areas showing symptoms. They ask about the symptoms’ history and family health. Sometimes, they take a small skin sample to rule out other issues. Looking for redness, scaling, and itching helps tell seborrheic dermatitis from dandruff.
Distinguishing Between Conditions
Differentiating seborrheic dermatitis from dandruff requires careful consideration. Doctors look at many factors to figure out the main issue. Seborrheic dermatitis might be tied to genetics or stress, while dandruff is often less severe. After understanding the conditions, they can suggest the right treatment. For more information, visit this resource.
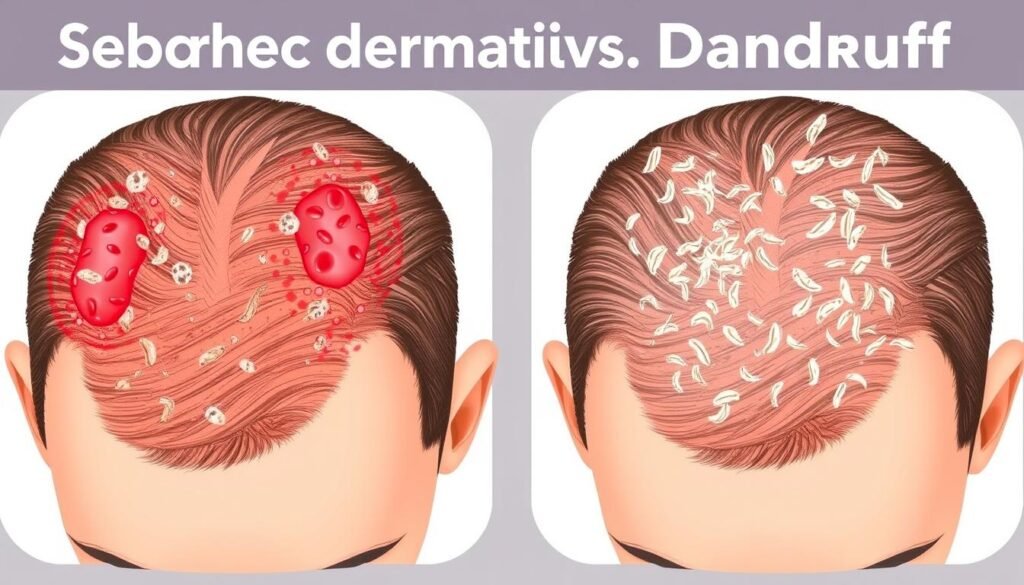
| Condition | Key Features | Common Affected Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Inflammation, severe scaling, red patches | Scalp, face, back, upper chest |
| Dandruff | Mild scaling, less inflammation | Mainly the scalp |
Treatment Options for Seborrheic Dermatitis
There are many ways to treat seborrheic dermatitis. We look at reducing symptoms and avoiding more outbreaks. Treatments include shampoo treatments, natural remedies, and medical treatments.
Shampoo Treatments
Medicated shampoos are key in fighting seborrheic dermatitis. They have ingredients like selenium sulfide and ketoconazole. Studies show these shampoos work well, with Ciclopirox helping 58% of users in 4 weeks.
The cost of these shampoo treatments is usually between $3 to $15. This makes them a budget-friendly choice for many.
Natural Remedies
Some prefer natural remedies like tea tree oil or aloe vera. People say these help ease symptoms. But, there’s not much scientific proof yet. Still, they can be a good side treatment.
Medical Treatments
If store-bought options don’t work, medical treatments might be needed. Doctors might suggest creams like pimecrolimus or tacrolimus. For tough cases, antifungal and steroid creams are used.
Roflumilast foam is also effective, clearing skin for many within 8 weeks. Side effects were rare. Sometimes, combining treatments works best for severe cases.
Treatment Options for Dandruff
Dandruff is a big concern for many. People look for effective treatments. Luckily, there are many options available, especially over-the-counter solutions. These products aim to ease symptoms, make the scalp healthy again, and bring comfort.
Over-the-Counter Solutions
Over-the-counter options are key in fighting dandruff. They have active ingredients to tackle dandruff’s main causes.
- Zinc Pyrithione: It fights fungi and bacteria, managing Malassezia yeast, a dandruff cause.
- Salicylic Acid: It removes dead skin, leading to a healthier scalp by reducing scaling.
- Selenium Sulfide: Targets yeast, cuts down on symptoms, and controls oiliness.
- Ketoconazole: A strong antifungal, ketoconazole shampoos are great against tough dandruff.
Using these shampoos regularly can lessen flaking and itching. This leads to a healthier scalp.
Alternative Treatments
Some prefer alternative treatments alongside over-the-counter methods. These remedies have varying support from science but can help in other ways.
- Dietary Adjustments: Adding omega-3s from fish and walnuts may cut down inflammation from dandruff.
- Herbal Applications: Tea tree oil and aloe vera are popular for their calming and antifungal effects.
- Mind-Body Therapies: Techniques like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, aiming at stress, might better scalp conditions, including dandruff.

Though over-the-counter shampoos are a main choice, exploring alternative treatments can give extra help. This is for those wanting complete care for their scalp health.
Prevention Strategies for Healthy Scalp
Keeping your scalp healthy is crucial to avoid dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Using effective prevention methods will improve your scalp’s health and your happiness. Follow a routine that includes daily care, right product use, and managing your lifestyle.
Daily Care and Maintenance
It’s important to wash your hair regularly to keep oil and dead skin at bay. Choose shampoos that are gentle and free of sulfates to reduce irritation. Here are key tips for daily care:
- Wash hair regularly to prevent buildup of oil and flakes.
- Opt for products that are free from harsh chemicals, bleaches, and alcohol.
- Consider incorporating antifungal shampoos containing Pyrithione zinc or Ketoconazole to fight yeast overgrowth.
Managing Risk Factors
It’s vital to control the risks that can worsen your scalp problems. Managing stress is incredibly important for your scalp. You can lower stress by:
- Practicing yoga or meditation to reduce stress.
- Eating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish and flaxseeds.
- Keeping hydrated and avoiding too much sun to protect your scalp.
Adding these prevention steps to your daily routine boosts scalp health. This way, you can fend off dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Be proactive for a healthier scalp and better life quality.
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff is key to managing them well. Although they both cause flaking and irritation, their causes and treatments vary. People who understand the difference can make better choices for their skin health.
Seborrheic dermatitis is seen in about 11.6% of people, and is more common in certain groups. Dandruff, on the other hand, affects half of adults globally. Recognizing triggers like stress helps manage symptoms. Luckily, both can be treated with medicated shampoos, natural approaches, and good skincare.
Realizing how crucial awareness and education are can improve lives. For more details on these conditions, check out understanding seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff. This resource advocates a complete method for keeping scalps healthy.